Virus Vs Virus Draw Circle
A community is experiencing an outbreak of an communicable diseases. As a contact tracer for the local public health office, you must utilize the case information to make up one's mind where the illness spread, who requires testing, and which cases crave further investigation. You volition use ArcGIS Insights to create charts and apply nonspatial analytical techniques to track the spread of the virus.
Requirements
- ArcGIS Insights
- Publisher or Administrator role in an ArcGIS system (get a costless trial)
Lesson Program
Create charts for contact tracingCreate charts that can exist used to trace the spread of a virus through a customs. |
|
Interpret relationships between casesEmploy the charts to translate how the virus has spread and make decisions about which cases require follow-up or testing. |
|
You will load and analyze example data from a customs that is experiencing a viral outbreak. Due to the sensitive nature of patient data, the information used in this analysis is based on a fictional customs. The data was created with an assumption that each case infects approximately two new cases, unless measures are taken to isolate afterward infection. The data besides assumes that male person and female cases are equally likely to be infected. The age of infected cases is affected by the locations where the cases interacted, rather than certain age groups being more than susceptible to infection. You will create charts that will permit you to perform contact tracing in the customs.
Open up an ArcGIS Insights workbook
Yous will starting time by downloading a workbook packet and importing it into ArcGIS Insights.
- Go to the Community outbreak particular on ArcGIS Online and click Download.
- Once the Goose egg file is downloaded, excerpt its contents to a folder that is easily accessible.
The item inside is an Insights workbook bundle containing patient case information and locations where each instance had close contact with other people.
- Go to Insights and click Sign in. Sign in to your ArcGIS Organizational account.
To admission Insights in ArcGIS Online, your system'due south administrator must grant you a license for it. If you lot don't accept an ArcGIS account or a license for Insights, you tin sign up for an ArcGIS gratuitous trial.
- If necessary, in the Welcome to Insights window, click Skip.
Next, y'all will import the packet you downloaded.
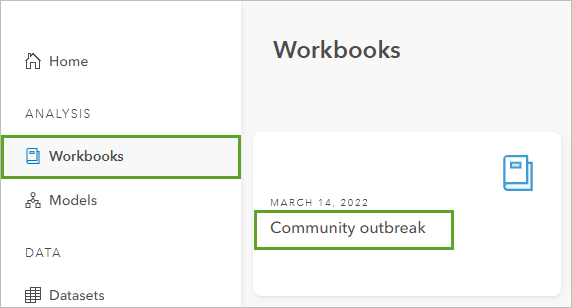
- On the abode page, click the Workbooks tab.
- Click Import, browse to the workbook you downloaded, and double-click Community_outbreak.insightswbk to add together it to Insights.
The workbook is loaded into Insights and appears on the Workbooks folio.
- On the Workbooks page, click Customs outbreak to open the workbook.
The workbook contains ii datasets, Example and Location, in the data pane. Both datasets are stored in Excel tables and were added to the workbook that you imported. Insights supports data from many sources, such every bit Excel, characteristic layers from ArcGIS Online, or data from ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World.
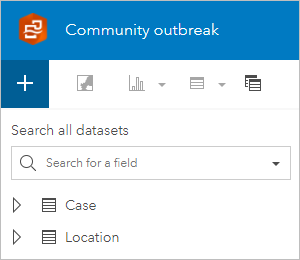
The workbook is titled Community outbreak and the page is named Contact tracing.
Side by side, you will use the datasets included in the workbook to create charts that brandish how the virus has spread through the community.
Create a link chart to trace contacts
Excel tables, like the datasets saved in the workbook bundle, are not spatially enabled when added to Insights. There are ways to speedily enable location on your data; however, since this data is not based on a real community, you volition focus this workflow on nonspatial charts. You will start with a link chart, which will prove the connections betwixt the cases in the community.
- In the data pane, click the arrow next to both the Case dataset and the Location dataset to show the fields.
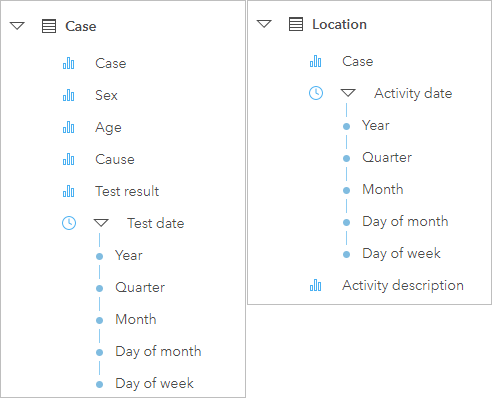
Case includes the fields Case, Sex, Age, Cause, Test consequence, and Examination date. Location includes the fields Case, Action date, and Activity clarification.
The Instance field refers to people who are beingness tested, or who are being monitored considering of close contact to someone who is being tested. The Case dataset lists each case once and provides details on each of the cases. Cases are identified by their household, sex (male person, female person, or other/adopt not to specify), and age range.
The Location dataset tracks the activities that each case participated in or locations where contacts were fabricated in the days preceding testing.
To track viral infections, y'all will want to see the relationship betwixt cases (including the cause of infection and test results) and reported contact locations. Since the information nearly each example is stored in a separate table from the reported activities, you lot volition start by joining the two datasets. The joined dataset will be used to create most of the charts in your analysis and volition allow all the charts to interact with each other, even when they reference data from different datasets.
- Higher up the information pane, click Create Relationship.

In the Create Relationships window, click Location and Case.
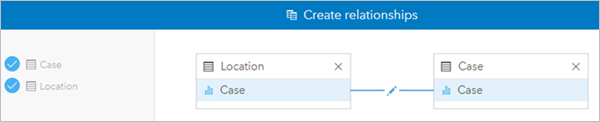
The datasets are added to the window. Joins must be made based on shared attributes in the two datasets. For your data, the Case fields were chosen as the joining fields, significant features with the same case value volition be joined.
By default, Insights performs inner joins, which ways that features that match for both datasets are included in the joined dataset. You lot want to keep the Location dataset as it is and add together the case data to each location entry, so yous will change the join type to a left join.
- On the line joining the two datasets, click edit.

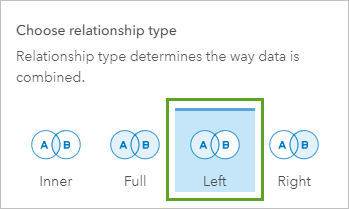
In the Edit Relationship window, y'all can cull to keep all information from both datasets, all data from the left dataset, or all data from the right dataset. The Location dataset is on the left side of the bring together, so that's the join type you lot volition utilize.
If you added the Example dataset first, and so that Location is on the right side of the join, you must cull Right every bit the join type instead.
- In the Edit Relationship window, nether Choose Relationship Type, click Left.
- In the Create Relationships window, click Finish.
- In the data pane, click the arrows abreast the datasets Case and Location to plummet them.
The joined dataset, called Location – Case, is added to the data pane. Joined datasets and other event datasets are indicated with an orange icon.

- In the data pane, expand Location – Case.
Now y'all will utilize the fields in the joined dataset to make charts that you can apply for contact tracing.
- Press and hold Ctrl and click Case and Activeness description.
The two fields are selected in the information pane and ready to be added to the carte du jour blazon of your pick. You add fields to cards by dragging them onto the empty page to admission the carte options.
- Elevate the selected fields onto the page and indicate to Chart to meet the options.
- Drop the fields onto Link Chart.
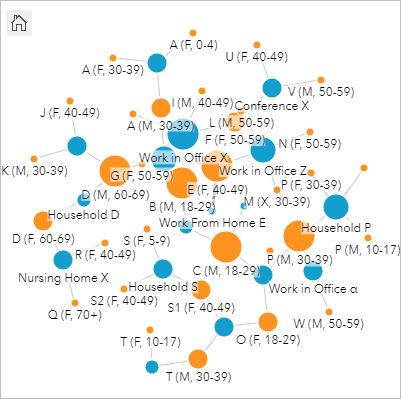
A link nautical chart is created showing the cases and locations, besides every bit the connections between them. Yous volition change some settings on the link chart to optimize your analysis.
- If necessary, click the link chart to activate it.
- On the toolbar, click the Fable push.
The Layer options pane displays properties for the chart.
The nodes, which stand for the cases and activity descriptions, are sized by graduated symbols using a method chosen centrality. The default centrality is measured by degree (the axis measure out appears in the Layer options pane, on the Options tab, nether the Graph options parameter).
The degree refers to the number of links a node has. A person who reported many activities or a place that many people reported visiting will have a larger degree than a person who reported few activities or a identify with a small number of people reported visiting.
- Under Size nodes using, expand the menu to see the other centrality options.
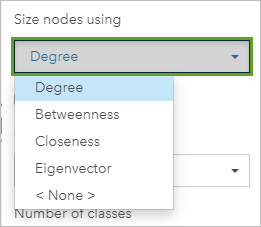
The following centrality options are available:
- Degree—The number of direct neighbors of the node.
- Betweenness—The extent to which a node lies on the shortest path between other nodes in the network.
- Closeness—The average of the shortest distance paths to all other nodes.
- Eigenvector—The measure of the influence of a node in a network based on its proximity to other of import nodes.
- Click Betweenness to change the axis measurement.
- Hover over a node on the nautical chart.
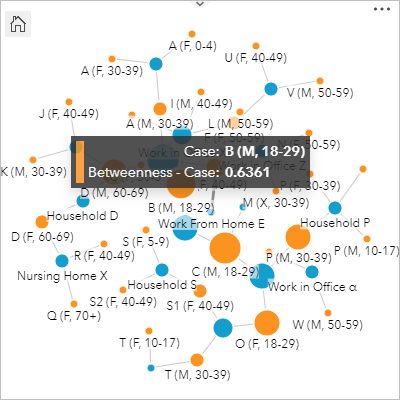
The hover pop-up tells you the example and betweenness for the node you pointed to. Past default, the centrality is normalized so the values range from 0 to 1. Next, you will configure the links on the nautical chart.
- In the Layer options pane, select the link connecting Case to Action clarification.
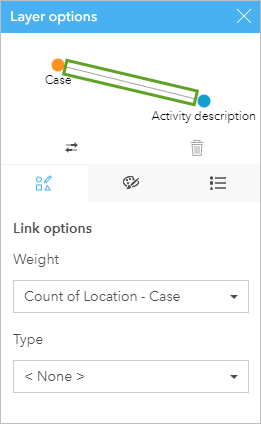
The Graph options are replaced with Link options.
- For Link options and for Weight, select <None>. For Blazon, select Crusade.
The links are styled using unique values based on the Crusade field. The lines are thin, then it can exist difficult to see which colors are used. You will change the line thickness.
- Click the Style tab to display the Link style options. For Thickness (min - max), change the minimum value to 2 px.
Finally, you volition configure the layout of the link chart.
- In the Layer options pane, click in an empty space near the link to deselect it.
The Graph style options announced in place of the Link mode options.
- For Layout, cull Radial.
The radial layout displays the nodes with the highest centrality near the centre, with links directed outward in an orbital blueprint.
- Close the Layer options pane and on the ribbon, click Save.

Yous take created a human relationship between ii separate datasets containing cases and locations and so created a link nautical chart. Adjacent, you lot will create charts that display how the virus has spread through the community and and then connect charts to the link nautical chart.
Create charts to clarify cases
The link nautical chart created in the previous pace shows the relationship between cases using shared locations. In this step, you will create charts that volition give you more information nearly the cases and the activities they reported prior to their test.
- In the information pane, expand Location - Example, if necessary.
- Select Activity date, drag it to an empty area on the page, and drop it on Fourth dimension Series.

A fourth dimension series graph is created showing the number of activities reported by all cases.
Next, yous will create a column nautical chart to testify the crusade of the potential infection for the cases. You will use the Case dataset rather than the joined dataset to ensure each case is only beingness displayed once.
- In the data pane, expand Case.
- Select Cause, drag it to an empty expanse on the page, point to Chart, and so driblet the field on Column Nautical chart.
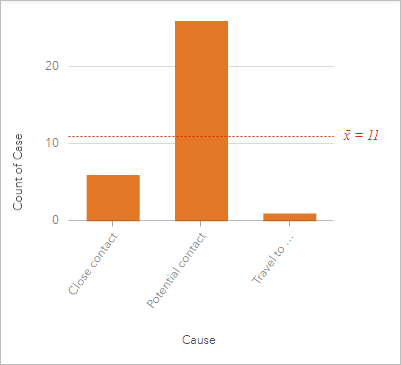
The cavalcade chart shows each cause (Close contact, Potential contact, and Travel to infected area) and the number of cases categorized for each. The columns on the chart are nevertheless color. You will modify the symbol to friction match the colors for the links on the link chart.
- Click the column chart to activate information technology, so click Fable to open the Layer options.
- Click Options.
- For Symbol blazon, choose Unique symbols.
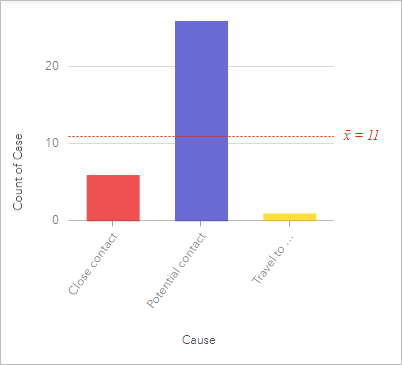
The chart is styled by unique symbols, using the aforementioned colors as the link nautical chart. The chart also shows the average count. You do not need the boilerplate count, and so y'all will remove it.
- Click Chart statistics.
- In the Chart Statistics pane, uncheck Hateful, and close the Nautical chart Statistics pane.
Next, you volition create a 2d column chart, this time to testify test results.
- In the Case dataset, select Test outcome, and drag it to the page to create a second column nautical chart.
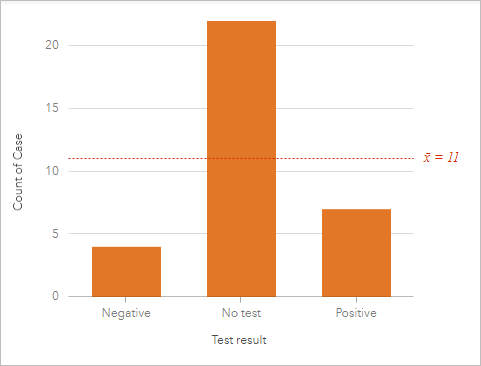
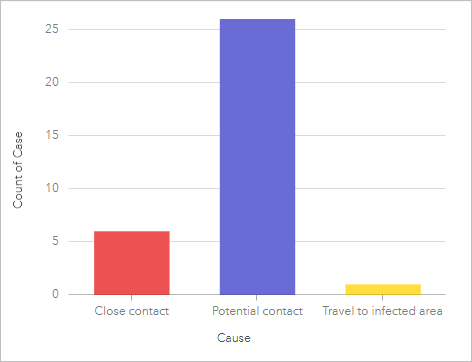
The column chart shows the test results (Negative, No test, and Positive) and the number of cases for each upshot.
The final step will exist to create a chart that shows the test results for each instance. You will create the chart using the joined dataset and so that it will also tell y'all the number of activities reported for each case.
- In the data pane, collapse Case and expand Location - Instance, if necessary.
- Select Case and Test upshot.
- Drag the fields to an empty surface area on the folio, point to Chart, and then drop the fields on Treemap.
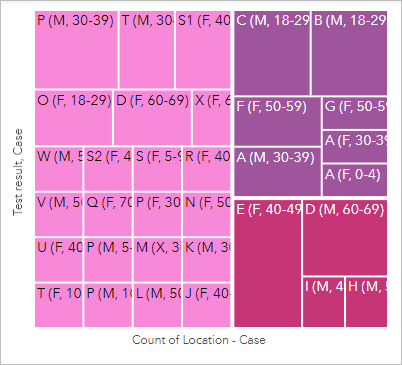
A treemap is created with different sized rectangles for each instance. The color of the rectangle is based on the test result, and the size is based on the number of activities reported for each case.
If your treemap does not show the cases grouped by test results, yous may have selected the fields in the incorrect order in the data pane. Click the Flip fields button on the y-axis to modify the orientation of the treemap.
- Click the treemap to activate it, if necessary, then drag the bottom handle to expand the treemap so the case values are visible.
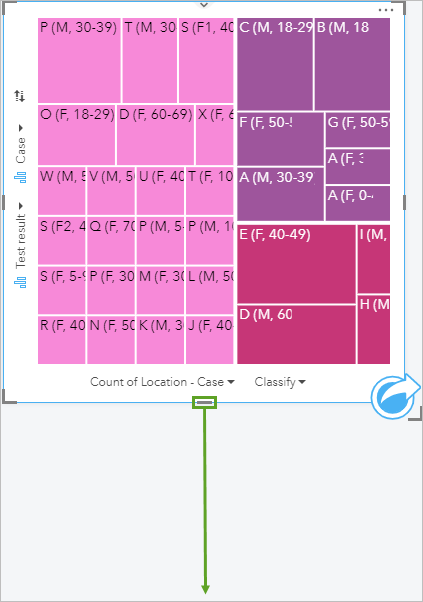
The treemap and second column chart both show exam results. Information technology would be helpful if the colors on the treemap were besides used on the cavalcade chart.
- Activate the 2nd column chart (Menu 4).
- Open the Layer options for Carte 4 and modify the Symbol blazon to Unique symbols.

- Click Chart Statistics and deselect Mean. Close the Chart Statistics pane.
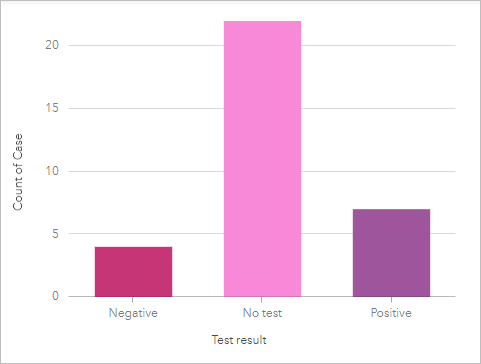
The test results on the cavalcade chart and the treemap are styled using the aforementioned colors.
- Click Hide on each of the cards to hide the card toolbar and make more space for the charts themselves. Alternatively, yous can add descriptive titles to the cards.
- Save your workbook.
Your page is now complete with several column charts, a treemap, and a link chart to help with contact tracing. Next, you lot volition use the charts yous made to analyze the viral spread through the community.
Translate relationships between cases
In ArcGIS Insights, the cards on your folio are interactive. You volition use the interactions betwixt cards to interpret patterns and draw meaningful conclusions from your data.
Determine viral spread
Y'all will use the charts created in the previous topic to determine how the virus has spread, where manual occurred, and who should exist tested or isolated to stop the spread.
The column chart for Crusade indicates at that place is only one instance of a known traveler.
- In the column nautical chart on Card iii, click the Travel to infected expanse column.
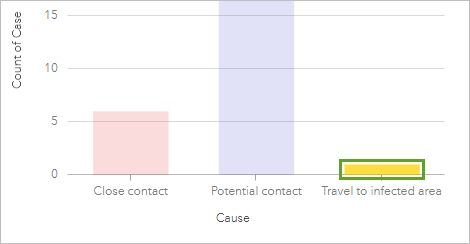
The other cards on the page update to testify the data linked to the selected column on the chart.
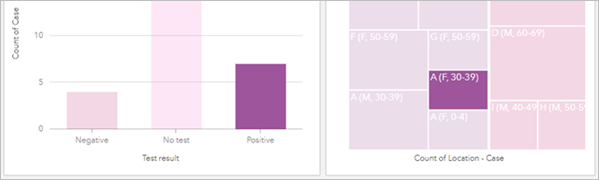
The treemap indicates the case linked to travel was A (F, 30-39), pregnant the case was for a female person historic period xxx to 39 in Household A. The treemap and column chart for test results indicate that the exam results for this case were positive, pregnant the patient was infected.
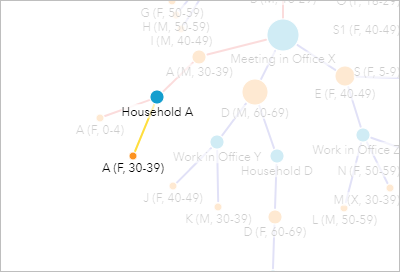
The link chart likewise shows A (F, 30-39) selected, and the direct connections betwixt the patient and the activities she reported. In the case of A (F, 30-39), only her household was reported.

A node on the time series indicates the date that A (F, 30-39) reported her activity (arriving habitation from travel to Household A) as three/half-dozen/2020. Since A (F, xxx-39) did not report whatever other activeness besides returning to her house, she is a low chance for transmitting the virus. You will look at the members of her household next.
- In the link chart, click the node for Household A to select information technology.
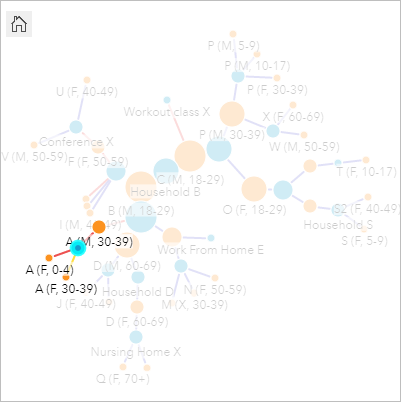
The link chart shows iii cases linked to Household A. The cases are besides selected on the treemap. A (F, 30-39) is the known traveler. A (Thousand, 30-39) and A (F, 0-iv) are the other members of her household. All iii household members have tested positive for the virus.
- Hover over the 3 selected rectangles on the treemap.
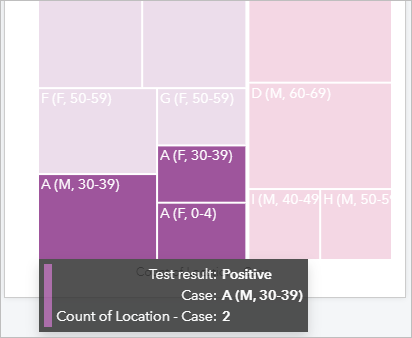
The hover pop-ups indicate that only one activity was reported for A (F, 30-39) and A (F, 0-4),, significant the only place they visited was their household (in other words, both cases were isolated after exposure to the virus). Case A (M, thirty-39) has two reported activities. You volition wait adjacent at where those activities were located to encounter whether there are others who may take been infected.
- On the treemap, click A (M, 30-39) to select information technology.
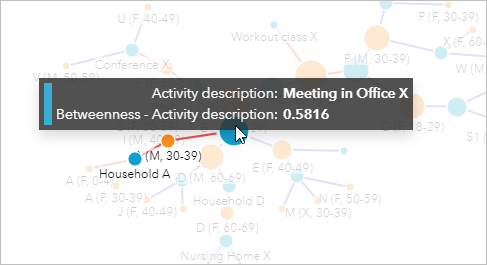
The link chart updates to testify the two links connected to A (Chiliad, 30-39).
Use the Zoom tools push or your curl wheel to zoom in on the link chart to see the nodes better.

- Hover over the two nodes for the activities linked to A (Thousand, 30-39).
I of the nodes is for Household A, which you already explored. The 2d is for Meeting in Role X. That node is larger than the others you've looked at and then far, which indicates it is a more important node for connecting nodes to each other (in other words, information technology has a more important office in spreading the virus).
- Click the node for Meeting in Office X.
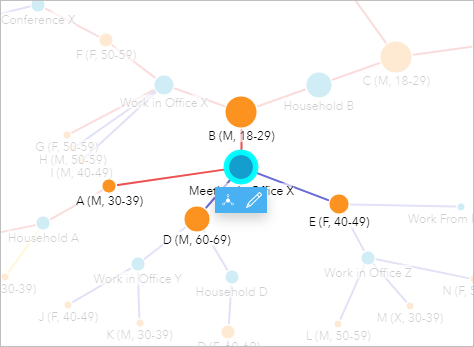
According to the time series graph, the meeting took place on 3/nine/2020, which is afterwards the fourth dimension when A (F, 30-39) returned from her trip.
Four cases are connected to Meeting in Office X. Await at the treemap to see more information about the cases. All 4 have been tested; 2 tested positive, including A (Thousand, 30-39), and two tested negative. The cases that tested negative practise not need to be pursued whatever farther.
- Click the node for E (F, 40-49) (1 of the negative cases).
Case Eastward (F, xl-49) reported 2 activities when she was tested: working from home and working in part Z. She too reported which coworkers she was in close contact with in office Z. Since E (F, xl-49) tested negative, those coworkers do not need to be tested. You will hide the leaf node in the chart to reduce ataxia. When you select a node in the link nautical chart, y'all can hide its leafage nodes, set it as a key node, or edit it.
- On the pop-up toolbar, click Hide Foliage Nodes.
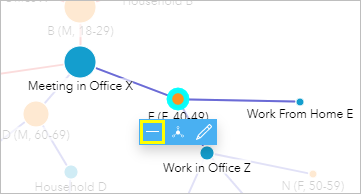
The link and node for Piece of work From Home E are hidden.
- Click the node for Piece of work in Office Z and hide its leaf nodes.
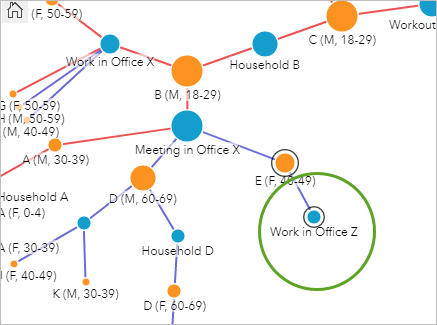
The nodes for the coworkers in Function Z are hidden. The other negative case was D (Thousand, 60-69).
- Click the node for D (M, 60-69).
D (M, 60-69) reported working in Function Y and staying in Household D. The link to Household D continues to instance D (F, 60-69), which in turn leads to Nursing Domicile X. Since D (Chiliad, 60-69) tested negative, none of these cases need to be tested considering of their connection to him.
- Hide the leaf nodes for Piece of work in Function Y and Nursing Home Ten.
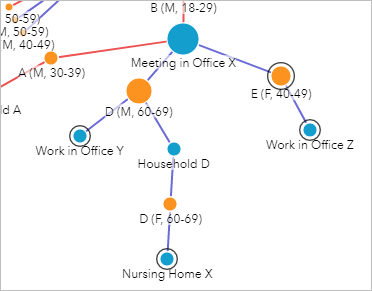
The other example from the meeting in Office X was B (M, xviii-29), who tested positive.
- Click B (Grand, eighteen-29) to come across his connections. The node has a loftier betweenness, which indicates this case is important for connecting all the nodes together.
B (M, 18-29) reported his household and Office X as the locations where he was in contact with others.
- Click Work in Office X to see the information for the coworkers.
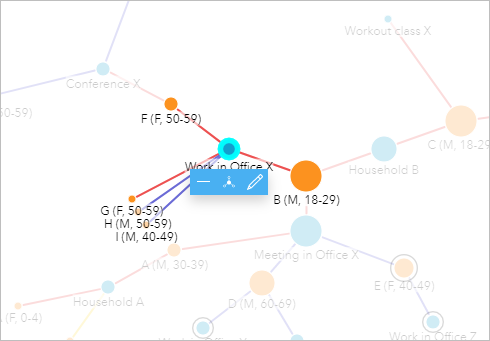
Co-ordinate to the treemap, H (M, 50-59) and I (K, 40-49) both tested negative. Therefore, at that place is no need to pursue their points of contact any further.
F (F, 50-59) and Yard (F, 50-59) both tested positive. There is no information for which locations Thousand (F, 50-59) visited since her exposure. That data volition demand to exist collected to fully trace additional points of contact.
F (F, 50-59) reported attending Conference X and coming into shut contact with two people.
- In the link chart, click Briefing 10.
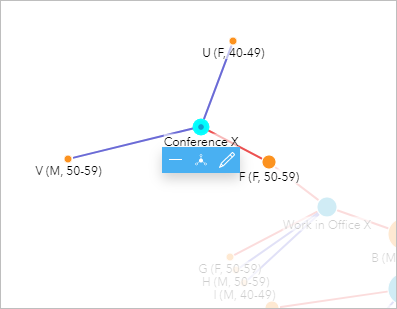
The two briefing attendees that came into contact with F (F, 50-59) were U (F, 40-49) and V (Yard, 50-59); in the treemap, these two cases are listed as No exam. Since F (F, 50-59) tested positive, those 2 cases will need to exist tested too. More information will likewise need to be gathered to make up one's mind whether other conference attendees should be tested or directed to cocky-isolate.
The other location that B (M, 18-29) reported was his household, which is connected to a 2d person who visited his household.
- Click the node for C (M, 18-29) (the 2nd node connected to Household B).
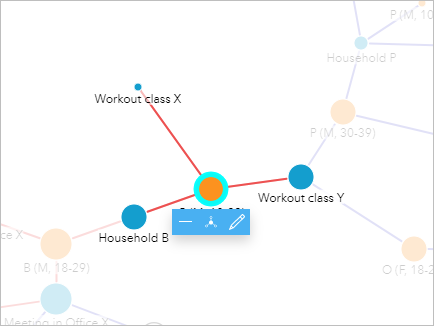
C (M, 18-29) is connected to Household B, plus two conditioning classes. His examination results are positive, which means there may be gamble to other people who attended the classes.
According to the nodes on the fourth dimension series, the activities reported were on three days: 3/8/2020, 3/ix/2020, and three/11/2020. Since C (1000, 18-29) probable contracted the virus from B (Thou, xviii-29), who came into contact with it through a meeting on three/ix/2020, the activeness on 3/8/2020 does not need to be pursued further.
- On the time series nautical chart, click the node for 3/8/2020 to see which action C (Grand, 18-29) reported earlier his exposure.

Co-ordinate to the link chart, Workout class 10 took place before C (M, 18-29) was exposed to the virus.
- In the link chart, click the node for C (M, 18-29) and click Hide foliage nodes.
Adjacent, you volition examine the second workout form.
- Click Workout class Y.
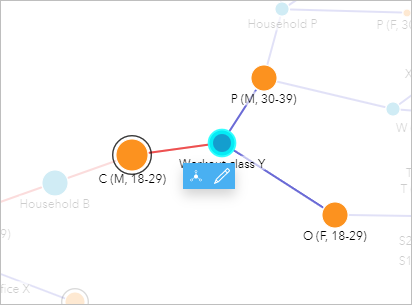
Two close contacts were reported, neither of whom take been tested. Since C (M, xviii-29) tested positive, tests should be conducted for both cases from the workout class. The two cases also accept reported contacts.
- Hold Ctrl and select the remaining location nodes (Household P, Work in Function α, Workout course Z, Household T, and Household S).
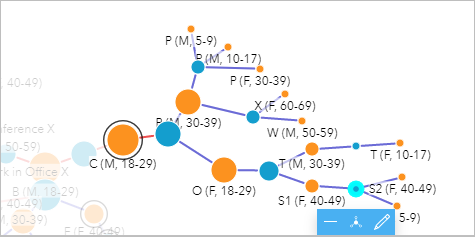
All the connections downstream from Conditioning class Y are selected. According to the treemap and the column chart with test results, none of the selected cases have been tested. Since there is a known link to a positive examination, farther action may be required for these cases, such as conducting tests or ordering self-isolation.
- Click an empty area on the link map to clear the choice.
- Save your workbook.
You have used charts to visualize and analyze instance data to determine which actions were required for the community. Link analysis is a powerful manner to clarify relationships in your data and visualize the interconnectedness of the cases that you are analyzing. If you have access to patient data and location, such as public health authorities, the post-obit are some of the options for mapping your data, you can perform the post-obit operations in Insights for mapping the information:
- Aggregate your case data into boundaries using spatial aggregation, such as neighborhoods or census blocks. Display the total number of cases in each boundary using graduated symbols with the Counts and Amounts (Size) symbol type or separate the number of cases by the full population of the boundary and brandish the proportions using graduated colors with the Counts and Amounts (Color) symbol blazon.
- Aggregate your case data into boundaries using spatial aggregation, and calculate z-scores to determine distance from the mean. The z-scores tin exist mapped using standard deviation nomenclature and help determine if there are clusters of high and depression values, indicating an outbreak in a sure area or low levels of cases in another.
Source: https://learn.arcgis.com/en/projects/track-virus-spread-with-arcgis-insights/
0 Response to "Virus Vs Virus Draw Circle"
Post a Comment